What is SH2db?
- SH2db is a curated structural biology database that contains information on all 120 human SH2 domains. SH2db provides instant access to user-friendly protein sequence/phylogenetic data as well as ready-to-use structural (pymol) files for rapid protein visualization and comparison.
What type of data can be found on the site?
- Protein wild type canonical sequences and sequence numbers from UniProt, structures and publication information from the Protein Data Bank and AlphaFold models from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database.
Generic numbers
- What are generic numbers?
- How were generic numbers assigned to SH2 domains?
When comparing the sequences of homologous proteins or species orthologs, residue to residue comparisons can be aided by the use of a numbering system that is generic for the whole protein family. Such a system can help researchers find quick reference points in the proteins instead of just using the protein sequence numbers. By using a structure based alignment for our numbering system, we can make sure that these reference points align not just on the sequence level but also in 3D space. For example, from the sequence alignment of the two closely related SH2 domains, ABL1 and ABL2, we can see that one residue differs in the bC segment. Instead of referencing them as R161 and L207 we can just say that there is a difference between the two sequences in position bCx48. Such a system can help indentify key functional positions and channel the focus of researchers on the similarities and differences between these homologous proteins.
Following the guidelines of the Ballesteros-Weinstein and subsequent GPCRdb generic numbering system of GPCRs, SH2db assigns generic numbers to the SH2 domains based on a structure based sequence alignment where residues aligning in 3D space get the same generic number assigned. We identified 6 β-strands and 2+1 α-helices (where the plus one helix is only present in STAT proteins) for which we could assign generic numbers to. In addition, we gave numbers to two Sheinerman residues that are located in the bBbC turn. For each segment, we identified the most conserved position between all human SH2 domains and assigned the x50 number to it. Residues on either side of the x50 position that belong to the same segment got sequentially numbered in a decreasing and increasing order, respectively. One exception is the position labeled bDx521 only present in STAT proteins. This residue does not have a structurally corresponding residue in the other proteins as it protrudes in between positions bDx52 and bDx53 similarily like bulged residues in GPCRs. Thus, we followed the numbering of bulges in GPCRs for this particular case. The segment ends where determined based on the manual observation of the backbone hydrogen-bond patterns in the available structures.
How are the structural superpositions done?
- We used the backbone coordinates of the 3 core β-strands (bB, bC, bD) for the superpositioning. The rest of the segments are more flexible compared to this core region and thus their inclusion resulted in suboptimal overall superpositionings.
Main features
- SH2db
- About
- Search Page
- Browse
- Charts
The landing page provides an overview of SH2db and the citation of the primary paper.
Additional information about the inspiration of SH2db as well as key structural elements of the SH2 domain to aid user analysis.
The search page provides a comphrensive alignment of all human SH2 domains. The key structural elements are highlighted, and specific proteins or residues can be iteratively filtered. The alignment is color coded based on the amino acid side chain polarity, and selected alignment, structures, or Pymol files can be dowloaded as needed.
This page provides an alternative filtering approach to observe SH2 domains based on protein family, gene name, or UniProt ID.
Collated ’ready-to-use’ information on features/statistics of the SH2 domain protein family.
Example cases
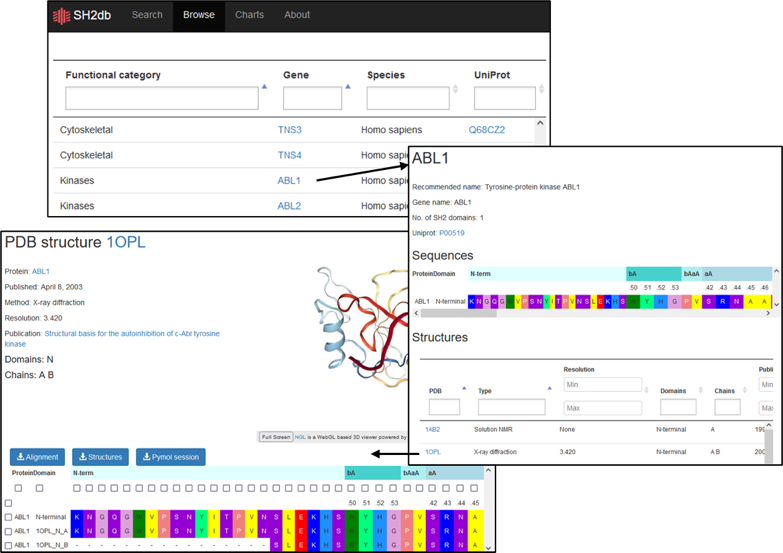
- Look up structures for a specific SH2 domain
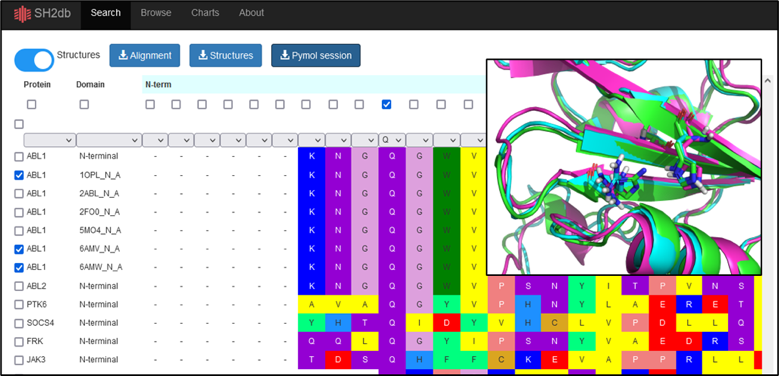
- Export pre-aligned structures of multiple SH2 domains into a Pymol session
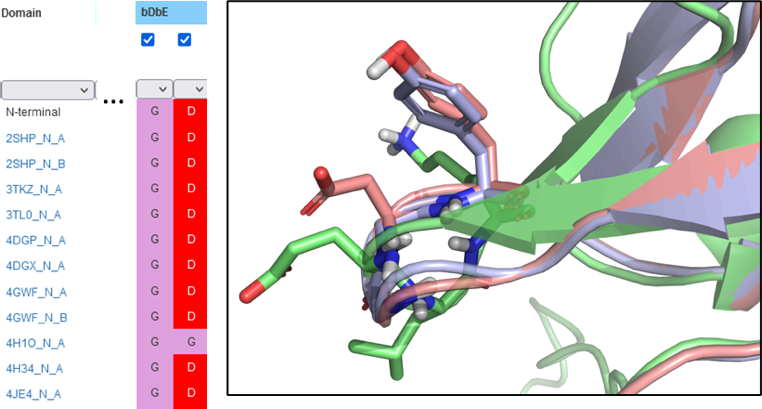
- Explore functional relevance of SH2 domain mutations
The SH2 domain for a known protein can be identified from the ’Browse’ page, either by entering the UniProt ID or gene name. All available structures (solved or predicted) will be displayed. Selecting the hyperlinked PDB will display the sequence as well as alignments, structures, and Pymol sessions for download.
From the Search page, toggle the ’Structures’ tab to ’on’. This will display all protien structures, and proteins can be filtered and selected in different approaches, such as through clicking the dropdown menu in the Protein column. Once selected, the alignments, structures, or Pymol sessions can be downloaded. Selecting residues with the checkboxes in the top row will highlight the residues as sticks in the resulting pymol session. Selecting the entries with the Uniprot IDs will default to exporting the corresponding AlphaFold models, when submitting structure-based download queries (pdb, or pymol session).
Identify the residue of interest in the SH2 domain, and scroll to the residue in the Search page. Filter for the mutation or new residue to examine other SH2 domains with that mutation, or select amino acids with similar polarity. Download the structures to examine the effects or explore the reference for functional characteristics of the SH2 domain.
Architecture and source code
- SH2db is built with the python based Django web framework using the PostgreSQL relational database.
- All our source code is open source and can be found on GitHub:
Browser compatibility
| OS |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| macOS | ✓ | ✓ | not tested | ✓ | not tested |
| Windows | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | not tested | not tested |
| Linux | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | not tested |
Additional information
- Liu paper (original starting point of the master alignment and functional grouping): Liu,B.A., Jablonowski,K., Raina,M., Arcé,M., Pawson,T. and Nash,P.D. (2006) The Human and Mouse Complement of SH2 Domain Proteins—Establishing the Boundaries of Phosphotyrosine Signaling. Mol. Cell, 22, 851–868.
Contact us
- You can contact us with any questions or suggestions regarding SH2db at sh2db
 ttk
ttk
 hu
hu