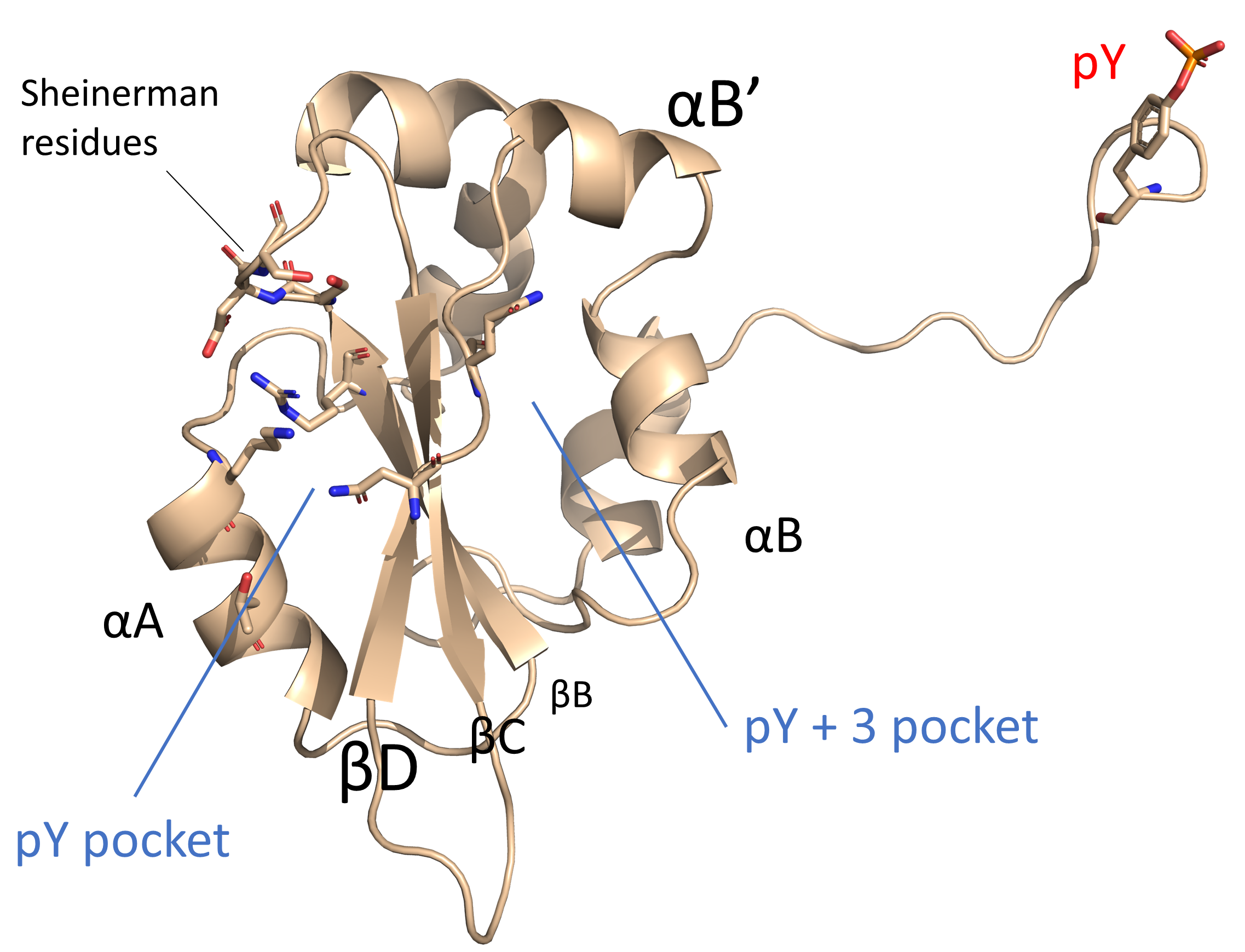
SH2 (Src Homology 2) domains are modular protein units that establish key protein-protein interactions and are therefore of high interest in drug discovery, particularly for oncological indications. SH2 domains recognize phosphotyrosine (pY)-containing peptide sequences, often as a mechanism for dimer formation, and subsequently regulate a range of cellular processes. A 2012 review by Liu et al., and our 2019 review with the Gunning group give a thorough overview of the general features of SH2 domains, the most important of which we have highlighted in Figure 1:
- The centerpiece of the conserved SH2 domain structure is the so-called αβββα motif, containing a central anti-parallel β-sheet (with the three β-strands conventionally labeled βB-βD) interposed between two α-helices (αA and αB).
- The β-sheet partitions the SH2 domain into two subpockets, referred to as the pY (phosphate-binding) and pY+3 (specificity) pocket.
- The Sheinerman residues are a group of 8 pY-interacting amino acids, which include the SH2 domain signature sequence FLXRXS (where X is a hydrophobic residue) with an invariant arginine in position βB50 (most conserved residue of the βB strand, see below for the generic numbering scheme introduced here).
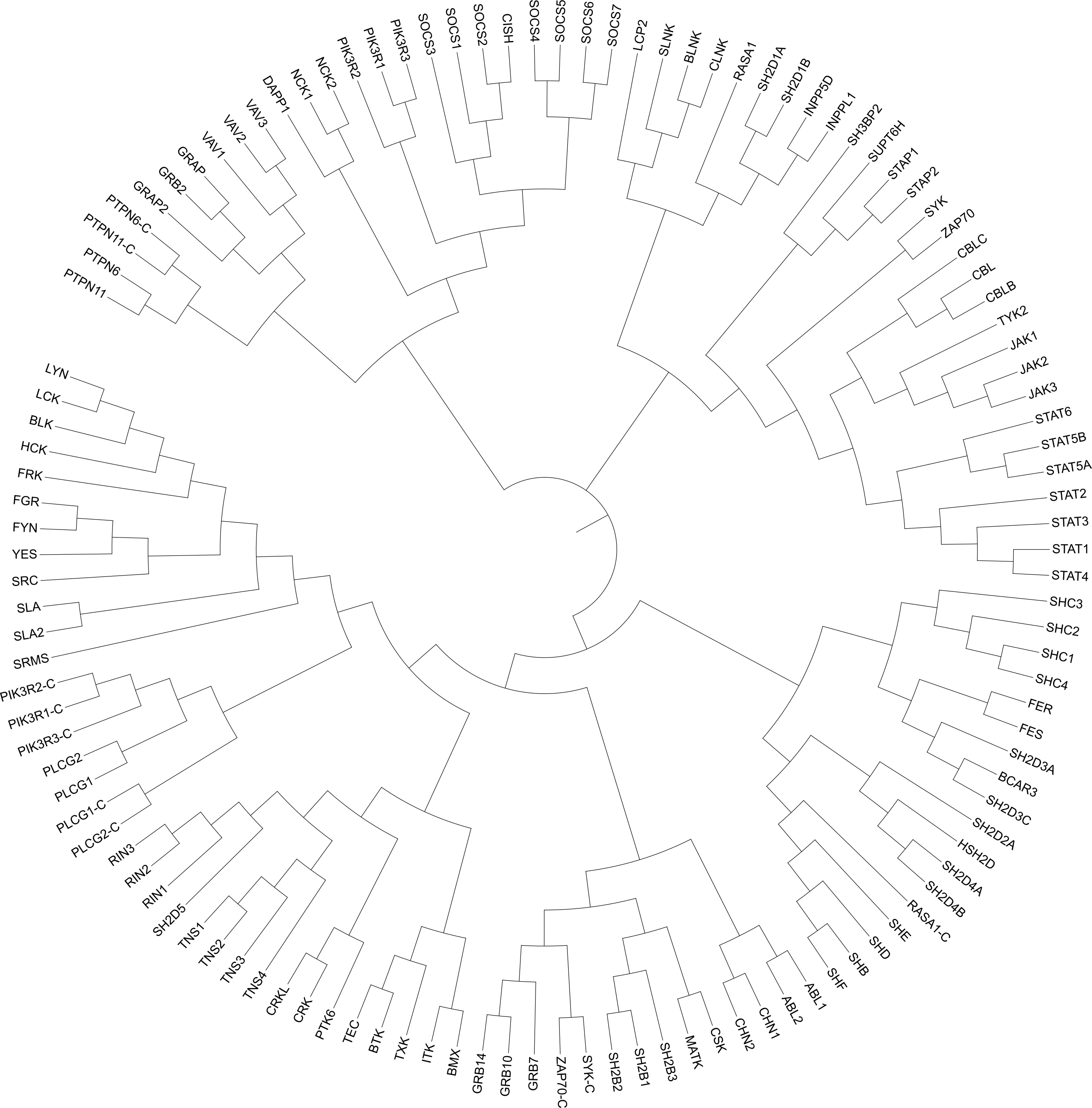
SH2db is an open-source database that aims to catalogue the structural information on SH2 domains in a way that is useful for medicinal chemists and structural biologists. Currently all human SH2 domains are collected and annotated (Figure 2). Grouping by functional categories is based on the work of Liu et al. SH2db is regularly updated with newly published PDB and AlphaFold structures of SH2 domains. All structures are aligned in two steps:
- The sequence is fitted onto a global sequence alignment that is based on the work of Liu et al. and refined based on the methodology of GPCRdb. The master alignment can be downloaded here.
- A structural alignment is then performed on the CA atoms of the central anti-parallel β-sheet.
Inspired by GPCRdb, we have introduced a generic residue numbering scheme for SH2 domains, as follows:
- Secondary structural elements are denoted by small letters (a for α helix and b for β strand), and labeled in the N-to-C-terminal direction by capital letters.
- Residue positions are numbered from 50 in both directions. In each structural element, position 50 denotes the most conserved sidechain. Numbers increase in the C-terminal direction and decrease in the N-terminal direction.
- As an example, the residue bB48 is two positions in the N-terminal direction from the most conserved residue of β strand B.
- Loops are named by merging the names of the structural elements they connect, e.g. loop aAbB connects α helix A to β strand B.
If you use SH2db in your work, please cite our primary paper:
SH2db, an information system for the SH2 domain.
Bajusz D., Pándy-Szekeres G., Takács Á., de Araujo E.D., Keserű G.M.
Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51, W542–W552
SH2db is an open-source project, maintained by the Medicinal Chemistry Research Group (@keserulab) in Budapest, Hungary.
You can contribute to the project via GitHub:
You can contact us with any questions or suggestions regarding SH2db at sh2db
![]() ttk
ttk
![]() hu
hu

